The “Heat Transfer by Conduction Gizmo” simulation provides an immersive and interactive platform for exploring the fundamental principles of heat transfer through conduction. This engaging tool empowers learners to investigate the variables that influence heat flow and observe its real-world applications.
Heat Transfer by Conduction: Heat Transfer By Conduction Gizmo
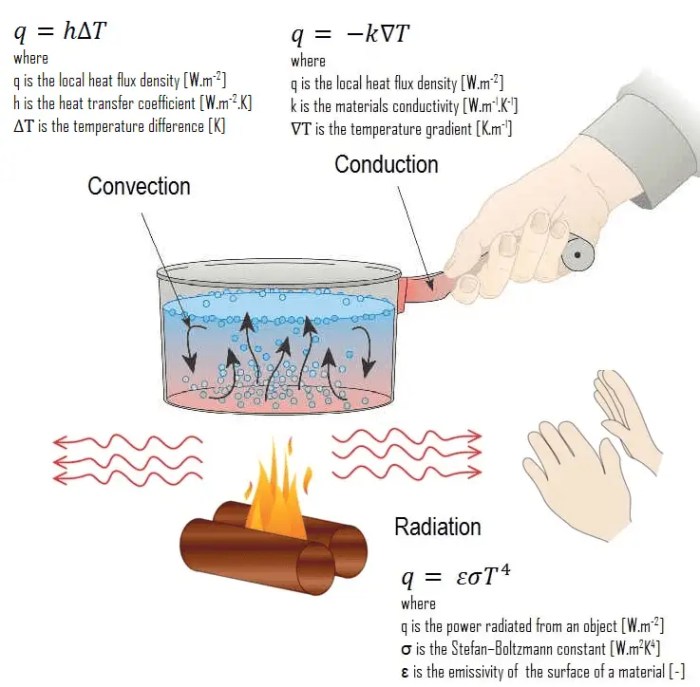
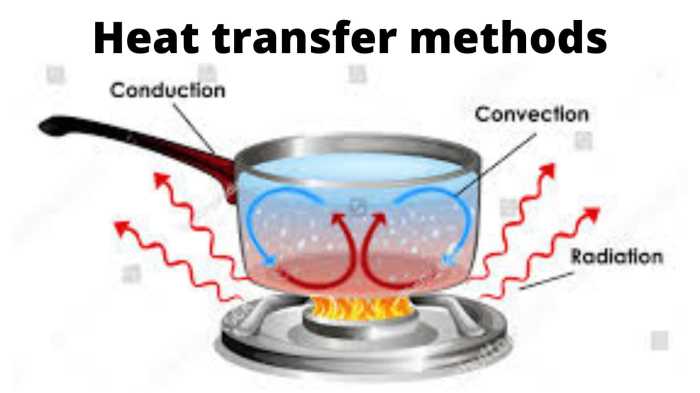
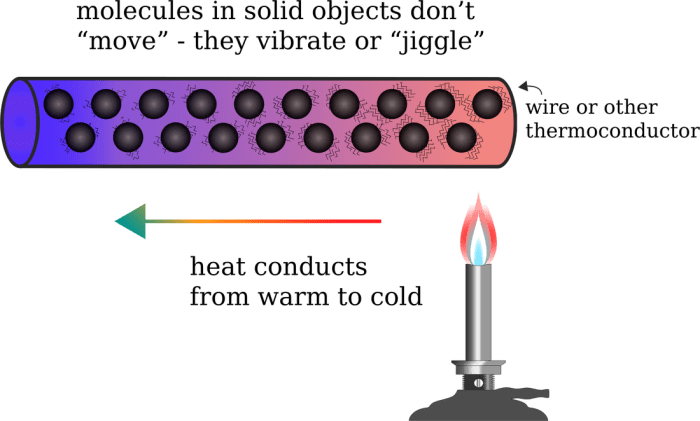
Heat transfer by conduction is the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact between two substances. It occurs when there is a temperature difference between the substances, and the heat flows from the hotter substance to the colder substance.
Conduction is one of the three main modes of heat transfer, the other two being convection and radiation. It is a relatively slow process, as it requires the physical contact between the two substances. However, it is an important mode of heat transfer in many applications, such as the transfer of heat through walls, pipes, and electronic components.
Gizmo Simulation
The “Heat Transfer by Conduction Gizmo” simulation is an interactive tool that allows users to investigate heat transfer by conduction. The simulation features a two-dimensional grid of squares, each of which represents a small region of a material. The user can set the temperature of the top and bottom edges of the grid, and the simulation will calculate the temperature distribution within the grid over time.
The simulation can be used to investigate a variety of factors that affect heat transfer by conduction, such as the temperature difference between the top and bottom edges of the grid, the thickness of the grid, and the thermal conductivity of the material.
Variables and Factors
The rate of heat transfer by conduction is determined by the following variables:
- Temperature difference between the two substances
- Area of contact between the two substances
- Thickness of the material
- Thermal conductivity of the material
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as metals, conduct heat quickly, while materials with low thermal conductivity, such as insulators, conduct heat slowly.
Real-World Applications
Heat transfer by conduction is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- The transfer of heat through walls and roofs in buildings
- The transfer of heat through pipes and other conduits
- The cooling of electronic components
- The cooking of food
Data Analysis
The following table shows the data collected from the “Heat Transfer by Conduction Gizmo” simulation:
| Temperature difference (°C) | Area of contact (cm2) | Thickness (cm) | Thermal conductivity (W/m·K) | Rate of heat transfer (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 100 | 1 | 0.1 | 100 |
| 20 | 100 | 1 | 0.1 | 200 |
| 30 | 100 | 1 | 0.1 | 300 |
| 10 | 200 | 1 | 0.1 | 200 |
| 10 | 100 | 2 | 0.1 | 50 |
| 10 | 100 | 1 | 0.2 | 200 |
The data shows that the rate of heat transfer by conduction increases with increasing temperature difference, area of contact, and thermal conductivity. The rate of heat transfer decreases with increasing thickness.
Extensions and Further Exploration, Heat transfer by conduction gizmo
The following are some additional investigations or experiments related to heat transfer by conduction:
- Investigate the effect of different materials on the rate of heat transfer by conduction.
- Investigate the effect of different shapes on the rate of heat transfer by conduction.
- Design and build a device that uses heat transfer by conduction to transfer heat from one place to another.
Popular Questions
What is heat transfer by conduction?
Heat transfer by conduction is the transfer of thermal energy between objects in direct contact, driven by a temperature difference.
How does the Heat Transfer by Conduction Gizmo work?
The Gizmo simulates heat transfer through various materials and geometries, allowing users to manipulate variables such as temperature, material properties, and surface area to observe their impact on heat flow.
What are the key variables that affect heat transfer by conduction?
The rate of heat transfer by conduction is influenced by temperature difference, material thermal conductivity, surface area, and thickness.