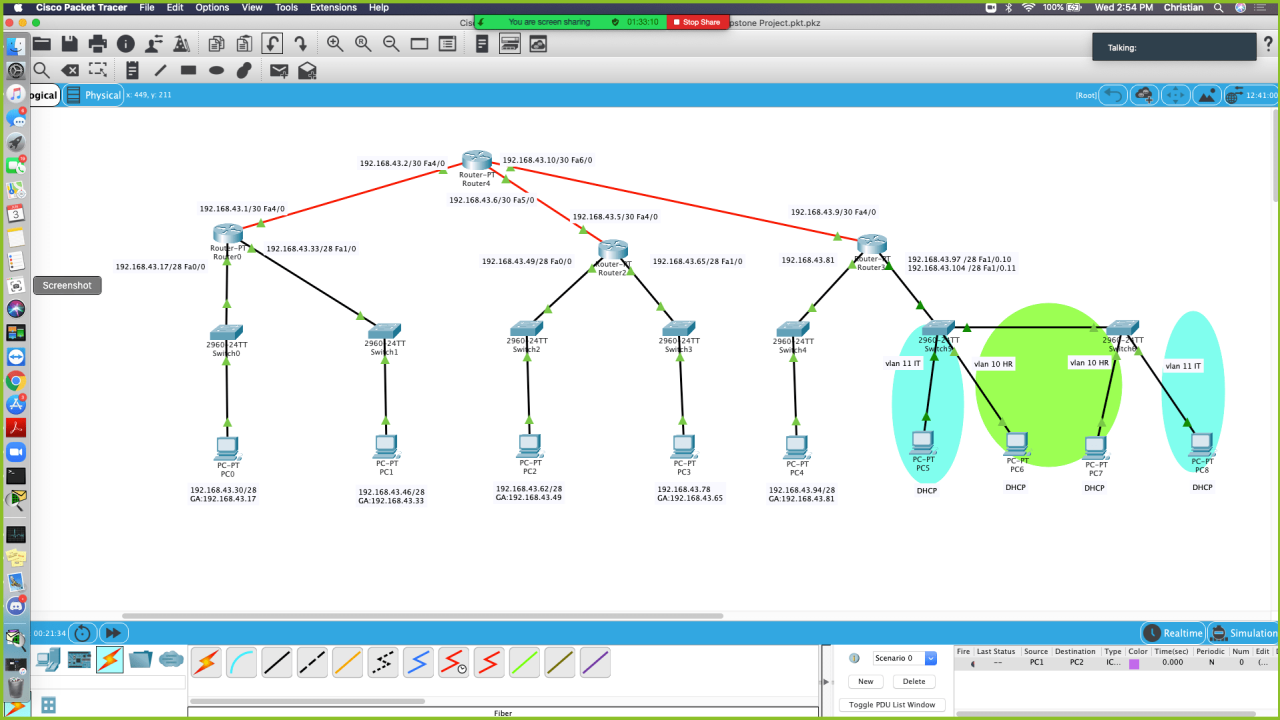
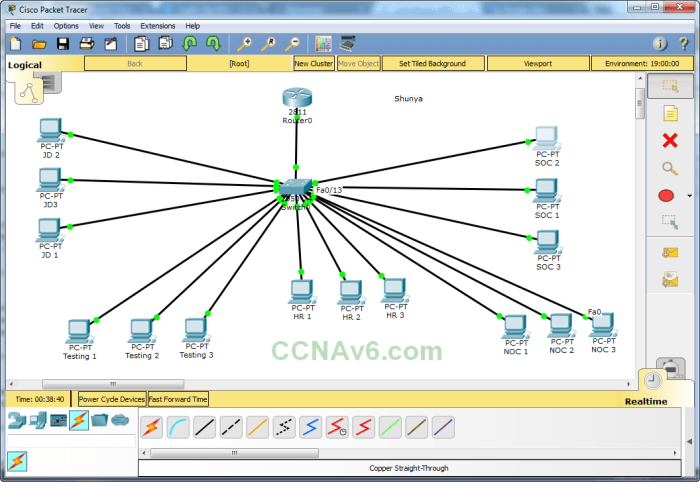
Simulation lab 8.1 module 08 subnets in cisco packet tracer – Embark on an immersive exploration of subnetting with Simulation Lab 8.1 Module 08 in Cisco Packet Tracer. This module provides a comprehensive understanding of subnetting, its significance in network design, and its practical implementation within a real-world network.
Through a captivating narrative, we delve into the intricacies of subnetting, empowering you with the knowledge and skills to optimize network performance and security. Join us as we unravel the complexities of subnet configuration, implementation, and troubleshooting, guiding you towards a mastery of this fundamental networking concept.
Subnets in Cisco Packet Tracer: Simulation Lab 8.1 Module 08 Subnets In Cisco Packet Tracer
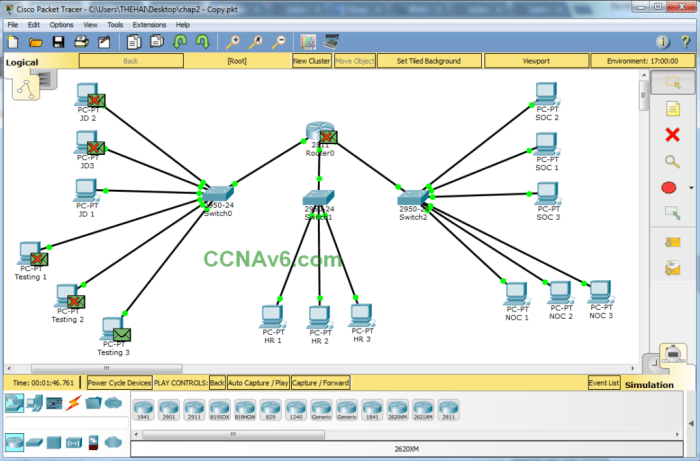
Subnetting is a crucial aspect of network design, enabling the efficient allocation and management of IP addresses. It involves dividing a larger network into smaller, manageable subnetworks, known as subnets.Subnetting offers several advantages:
-
-*Improved network performance
Subnets reduce network traffic congestion by limiting the broadcast domain.
-*Enhanced security
Subnets isolate different parts of the network, making it harder for unauthorized access and malware to spread.
-*Scalability
Subnetting allows for easy expansion of the network without the need to reconfigure the entire network.
Subnet Configuration
Subnetting involves two key parameters:
-
-*IP address
The unique identifier assigned to each device on the network.
-*Subnet mask
A 32-bit binary number that determines the network portion and host portion of the IP address.
The subnet mask is applied to the IP address using a bitwise AND operation. The resulting network address identifies the subnet, while the host portion identifies the specific device within the subnet.
Cisco Packet Tracer Simulation, Simulation lab 8.1 module 08 subnets in cisco packet tracer
Cisco Packet Tracer is a powerful simulation tool that allows users to create and configure virtual networks. It provides a realistic environment for experimenting with different network designs, including subnetting.To create a subnet in Packet Tracer, follow these steps:1.
-
-*Create a new network
Click on “File”
- > “New” to create a new network.
- 2.
- 3.
- > “IP Configuration.” Assign IP addresses and subnet masks according to the desired subnet configuration.
- 4.
-*Add devices
Drag and drop devices (e.g., routers, switches, hosts) onto the workspace.
-*Configure IP addresses and subnet masks
Right-click on each device and select “Configure”
-*Connect devices
Use Ethernet cables to connect the devices as per the network design.
Subnet Implementation
Subnets are implemented in real-world networks using routers and switches. Routers connect different subnets and route traffic between them, while switches connect devices within a subnet.Subnet implementation involves:
-
-*VLANs
Virtual LANs (VLANs) can be used to create logical subnets within a physical network.
-*Routing protocols
Routing protocols (e.g., RIP, OSPF) allow routers to exchange routing information and maintain connectivity between subnets.
-*Firewalls
Firewalls can be used to control traffic between subnets, enhancing security.
Troubleshooting Subnet Issues
Common subnet configuration errors include:
-
-*Incorrect subnet mask
Using an incorrect subnet mask can result in devices being unable to communicate.
-*Overlapping subnets
Assigning overlapping subnets can cause IP address conflicts and network issues.
-*Incorrect default gateway
Devices must have the correct default gateway configured to access the internet or other subnets.
Troubleshooting techniques:
-
-*Use network monitoring tools
Tools like Ping and Traceroute can help identify connectivity issues.
-*Check IP configurations
Verify that all devices have valid IP addresses and subnet masks.
-*Examine routing tables
Ensure that routers have the correct routing information to forward traffic between subnets.
Best Practices for Subnet Design and Implementation
-
-*Plan the subnet structure
Determine the number and size of subnets based on the network requirements.
-*Use appropriate subnet masks
Choose subnet masks that provide the necessary number of host addresses.
-*Avoid overlapping subnets
Ensure that subnets do not overlap to prevent IP address conflicts.
-*Document the subnet configuration
Keep a record of the subnet configuration for future reference and troubleshooting.
User Queries
What is the primary purpose of subnetting?
Subnetting allows for the division of a large network into smaller, more manageable segments, enhancing network performance and security.
How do I calculate the subnet mask for a given subnet?
To calculate the subnet mask, you can use the following formula: Subnet Mask = (2^n) – 1, where n represents the number of bits borrowed from the host portion of the IP address.
What is the role of a router in subnet communication?
Routers play a crucial role in subnet communication by forwarding packets between different subnets, ensuring seamless data transmission across the network.