Choose the reaction that represents the combustion of c6h12o2 – Combustion of C6H12O2: A Comprehensive Guide
Combustion reactions play a crucial role in various scientific and industrial processes. One such reaction involves the combustion of C6H12O2, which exhibits unique characteristics and applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of C6H12O2 combustion, exploring its products, energy release, influencing factors, and practical applications.
Combustion Reaction
Combustion is a chemical reaction that involves the rapid oxidation of a substance, usually in the presence of oxygen, releasing heat and light. The chemical components involved in combustion are fuel (the substance being oxidized), oxygen (the oxidizing agent), and heat (the energy required to initiate the reaction).
The fuel can be a solid, liquid, or gas, and the oxygen can come from the air or from a pure oxygen source.
The combustion of C6H12O2, commonly known as glucose, is a classic example of a combustion reaction. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
C6H12O2 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
Products of Combustion: Choose The Reaction That Represents The Combustion Of C6h12o2
The primary products formed during the combustion of C6H12O2 are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). These products are released into the atmosphere as gases.
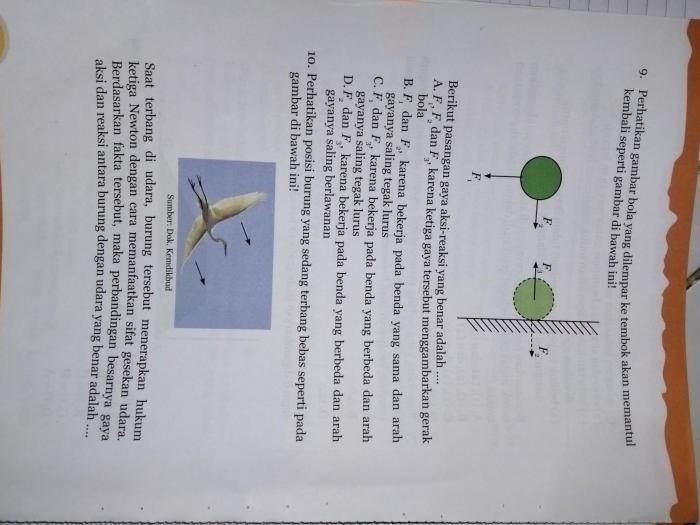
Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless, and non-toxic gas. It is a greenhouse gas, meaning it contributes to global warming by trapping heat in the atmosphere. Water is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless liquid. It is essential for life and is found in all living organisms.
Energy Release
The combustion of C6H12O2 releases a significant amount of energy, which is calculated using the enthalpy change (ΔH) of the reaction. The enthalpy change is a measure of the heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction. For the combustion of C6H12O2, the enthalpy change is -2803 kJ/mol.
This energy can be used to power engines, generate electricity, or provide heat for homes and businesses. The combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is a major source of energy worldwide.
Factors Affecting Combustion

The combustion of C6H12O2 is influenced by several factors, including:
- Temperature:Combustion requires a certain amount of heat to initiate and sustain the reaction. The higher the temperature, the faster the combustion will occur.
- Oxygen concentration:The amount of oxygen available affects the rate and completeness of combustion. The higher the oxygen concentration, the faster and more complete the combustion will be.
- Fuel composition:The type and composition of the fuel can also affect combustion. Fuels with a higher carbon content tend to burn more slowly and produce more soot than fuels with a lower carbon content.
- Pressure:The pressure of the environment can also affect combustion. Higher pressure can increase the rate of combustion, while lower pressure can slow it down.
Applications of Combustion
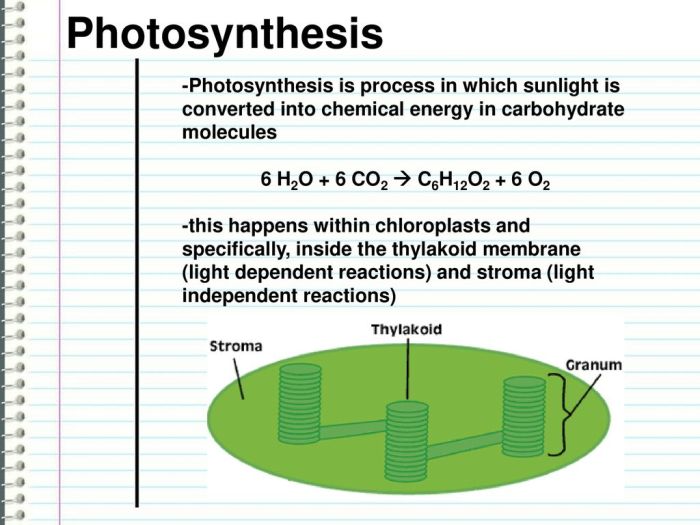
The combustion of C6H12O2 has numerous applications, including:
- Power generation:The combustion of C6H12O2 is used to generate electricity in power plants. The heat released from the combustion is used to boil water, which creates steam. The steam is then used to drive a turbine, which generates electricity.
- Heating:The combustion of C6H12O2 is also used to provide heat for homes and businesses. Natural gas, which is primarily composed of methane (CH4), is a common fuel used for heating.
- Transportation:The combustion of C6H12O2 is used to power vehicles, such as cars, trucks, and airplanes. Gasoline and diesel fuel are common fuels used in transportation.
Advantages:
- C6H12O2 is a readily available and relatively inexpensive fuel.
- The combustion of C6H12O2 releases a significant amount of energy.
- C6H12O2 is a relatively clean-burning fuel, producing fewer pollutants than other fossil fuels.
Disadvantages:
- The combustion of C6H12O2 produces greenhouse gases, which contribute to global warming.
- The combustion of C6H12O2 can release harmful pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter.
- The supply of C6H12O2 is finite, as it is derived from fossil fuels.
FAQ Overview
What is the chemical equation for the combustion of C6H12O2?
C6H12O2 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
What are the primary products of C6H12O2 combustion?
The primary products are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
How is the energy released during C6H12O2 combustion utilized?
The energy released can be used for various purposes, such as heating, power generation, and transportation.