Select all of the accurate descriptions and/or definitions of cytokinesis. Cytokinesis is the process of dividing the cytoplasm of a cell into two or more daughter cells. It is the final stage of cell division and is essential for the proper distribution of organelles and genetic material to the daughter cells.
There are two main mechanisms of cytokinesis: animal cell cytokinesis and plant cell cytokinesis. Animal cell cytokinesis involves the formation of a cleavage furrow, while plant cell cytokinesis involves the formation of a cell plate.
Cytokinesis is a complex process that is regulated by a variety of factors, including the cell cycle, the cytoskeleton, and the cell membrane. Errors in cytokinesis can lead to a variety of problems, including cell death, developmental abnormalities, and cancer.
Cytokinesis: General Overview
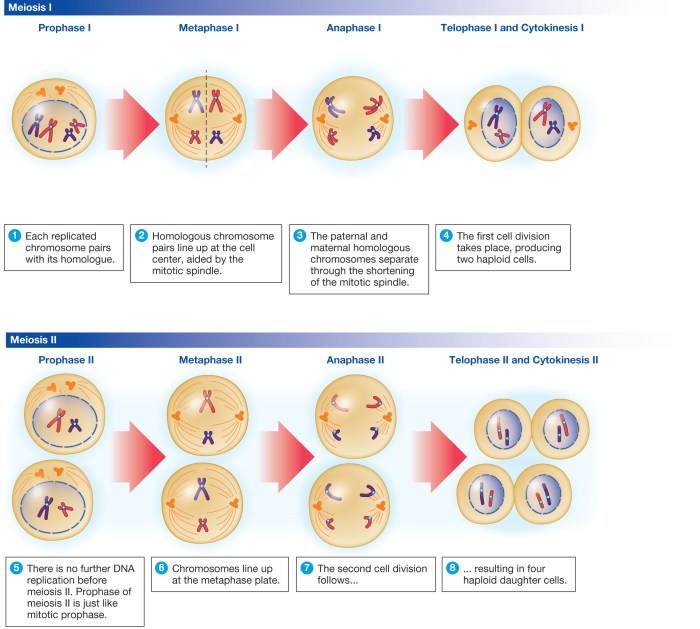
Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division, resulting in the physical separation of the cytoplasm and organelles into two distinct daughter cells. It ensures the equitable distribution of cellular components and genetic material to each daughter cell. Cytokinesis involves a series of complex and tightly regulated processes that vary depending on the cell type and organism.Cytokinesis
can be traced back to the early 19th century, when scientists first observed the division of cells under a microscope. Over time, advancements in microscopy and molecular biology have provided deeper insights into the mechanisms and regulation of cytokinesis.
Mechanisms of Cytokinesis
Two primary mechanisms of cytokinesis exist: Animal Cell Cytokinesis:
- Involves the formation of a cleavage furrow, a constriction of the cell membrane that gradually pinches off the cytoplasm.
- Driven by the assembly and contraction of a ring of actin and myosin filaments, known as the contractile ring.
Plant Cell Cytokinesis:
- Forms a cell plate, a new cell wall that grows inward from the center of the cell, dividing the cytoplasm.
- Involves the fusion of Golgi-derived vesicles containing cell wall material.
Molecular components essential for cytokinesis include microtubules, actin filaments, myosin motors, and regulatory proteins such as RhoA and Cdc42.
Regulation and Control of Cytokinesis: Select All Of The Accurate Descriptions And/or Definitions Of Cytokinesis
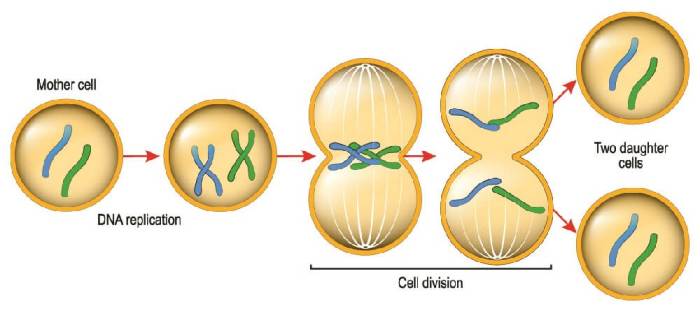
Cytokinesis is tightly regulated to ensure proper cell division. Cell cycle checkpoints monitor the completion of DNA replication and spindle formation before initiating cytokinesis. Signaling pathways, such as the Aurora B kinase pathway, coordinate the assembly and contraction of the contractile ring.Errors
in cytokinesis regulation can lead to abnormal cell division, resulting in aneuploidy (abnormal chromosome number) and potential diseases such as cancer.
Comparative Analysis of Cytokinesis in Different Organisms
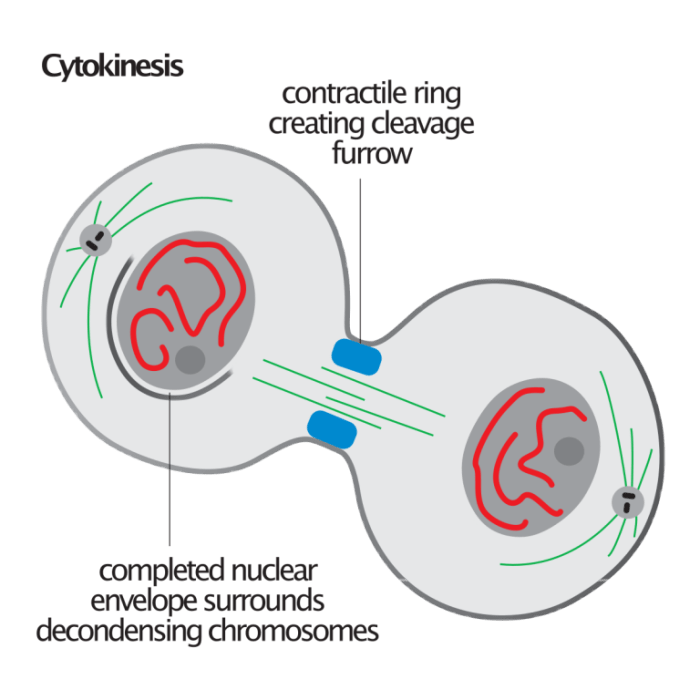
Cytokinesis mechanisms vary across different organisms: Bacteria:Binary fission, a simple division into two equal daughter cells, occurs through the formation of a septum. Yeast:Budding, where a new daughter cell grows as an outgrowth from the parent cell. Mammalian Cells:Animal cell cytokinesis, with the formation of a cleavage furrow.These
variations reflect evolutionary adaptations to different cell types and organismal requirements.
Applications and Significance of Cytokinesis
Cytokinesis research has applications in biotechnology and medicine:
- Biotechnology:Cytokinesis can be manipulated to create cell lines with specific characteristics for research and therapeutic purposes.
- Medicine:Understanding cytokinesis can lead to new therapies for diseases related to abnormal cell division, such as cancer.
Future research directions include exploring the role of cytokinesis in stem cell differentiation and tissue regeneration.
FAQs
What is cytokinesis?
Cytokinesis is the process of dividing the cytoplasm of a cell into two or more daughter cells.
What are the two main mechanisms of cytokinesis?
The two main mechanisms of cytokinesis are animal cell cytokinesis and plant cell cytokinesis.
What are some of the factors that regulate cytokinesis?
Some of the factors that regulate cytokinesis include the cell cycle, the cytoskeleton, and the cell membrane.
What are some of the consequences of errors in cytokinesis?
Some of the consequences of errors in cytokinesis include cell death, developmental abnormalities, and cancer.